Role Mapping : Critical Intersection on the Road to ERP Implementation
Role Mapping is a key step in the ERP implementation process. The completion of this work creates the framework that allows users to access the system, identifies the system components for which each user will require training, and ultimately contributes to the realisation of targeted business benefits. So what exactly is role mapping and what are the key do-wells to ensure that this work is successful?
Some background information initially - the business process teams are responsible for developing the new business design as part of the overall process redesign. At the end of this phase they will have developed a list of business process flows and information about the ERP solution with related activities and master data, but they will also have developed a list of associated ‘roles’. To simplify, a role is the part an employee plays in completing work and is a subset of tasks (system and non-system) carried out by a job. A role description can be part of a job description but a role title does not usually equal a job title, because jobs are typically comprised of one or more roles within the ERP system.
Role mapping defines how roles are connected to process activities and which roles are connected to what people (and jobs) in the ‘to-be’ organisation. Role Mapping results in the assignment of security roles and other user-specific settings to the employees that will use the ERP system being deployed. It is also a critical input into the key step of developing a training curriculum based on the roles that have been developed and the development of training content. The complexity of the output from Role Mapping work is evidenced by a recent role mapping implementation we completed in an organisation where the final output resulted in the mapping of approximately 100 roles against in excess of 320 different job titles!
Role Mapping typically involves a series of discussions with management and functional leads on the project to map jobs to the identified roles. There is usually a series of iterations during this process which will result in a re-definition of the roles until such time as the management is comfortable with the constitution of each job in the organisation. It is an important process as it provides management with a clear understanding as to how the new design will impact on existing jobs and starts the process of mitigating the impact of identified changes in jobs.
A successful Role Mapping exercise ensures that:
- Each user will have a clearly defined set of system tasks that they will need to perform allied with the appropriate system access.
- The Security and Testing Team will have the input they require to set up and test role-based access based on the outcomes of the role-mapping process.
- It provides critical input to the Training team in determining appropriate instructional strategy and content for end-user training and provides the foundation for the training needs analysis. It also permits the development of the training curriculum and confirmation of the training course schedule.
- It starts the process of considering the transition steps that need to be taken where jobs have been impacted by the design.
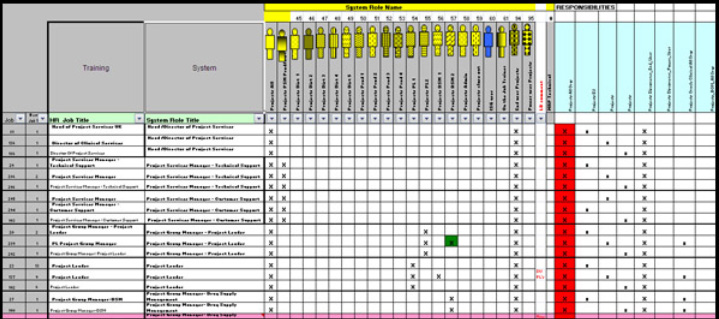
Fig 1: A typical Job to Role Matrix
Here are some key reminders that need to be considered in order to complete role mapping successfully:
- Role Mapping needs to be started as soon as possible after the completion of the design phase of the project – delaying the process will impact on the execution of the training plan.
- It is important to assemble a multi-functional team to execute role mapping owing to the complexity of this work. At a minimum this will include representatives from the change management team, the solutions architects, the security manager and the specialists who will configure the security profiles.
- The outputs from Role Mapping need to be validated by the business managers as they are a key step in the definition of the to-be job roles in the post-implementation organisation.
- It is critical to maintain consistency between the security profiles and the development of the training material – it is vital for user confidence that what they are trained on is equivalent to what they can access and see in the system.
In the rush to get from design closure to the completion of build and the start of testing the solution, the key step of role mapping can often be ignored until it is too late. But role mapping is a key step in any ERP project to ensure that security profiles are developed and an effective training curriculum is implemented – all necessary towards the goal of securing business benefits.
This blog post was written by Sean Jackson, Managing Director at Lumenia. If you would like further information on Role Mapping or any aspect of ERP Implementation please send an e-mail to Sean Jackson.


